Primocin®
| Product | Unit size | Cat. code | Docs. | Qty. | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Primocin® Antimicrobial agent for primary cells |
Show product |
250 mg (5 x 1 ml) 500 mg (10 x 1 ml) 1 g (1 x 20 ml) |
ant-pm-05
|
|
Antimicrobial agent for primary cells
Primocin® is designed to offer complete protection of primary cells from microbial contamination. Primocin® is a broad-spectrum antibiotic formulation that is gentle on your cells but lethal to the microbes. There are a number of common sources of microbial contamination especially in the isolation of primary cells from both animal and human tissue, including commensal flora and/or subclinical infections.

Use of Primocin® in primary cell cultures
Key Features:
- Active against bacteria, mycoplasma, and fungi
- A common addition to various standardized primary cell culture protocols
- Used throughout culturing process (e.g. culture media, wash solutions, and biopsy storage media)
- Highly cited in the literature
Primocin® is composed of four compounds, of which three, act directly on Gram-positive bacteria, Gram-negative bacteria, and mycoplasmas. The primary mode of action for these compounds is to block microbial DNA and protein synthesis. The fourth compound in Primocin® eradicates fungi, including yeasts, by directly targeting processes at the fungal membrane.
Primocin® is successfully used in many types of primary cell cultures (see citations) including:
- Differentiated mouse- and human-derived cells such as astrocytes and immune cells (e.g. natural killer cells)
- Stem cells such as mouse- and human-derived embryonic and pluripotent stem cells
- 3D cellular models (i.e. organoid and spheroids) such as colon epithelial and carcinoma organoids
Primocin® is made in-house at InvivoGen and is of the highest quality with rigorous quality control performed to ensure the absence of lot-to-lot variation.
Note: Primocin® is a trademark of InvivoGen registered with the United States Patent and Trademark Office and foreign equivalents.
All InvivoGen products are for internal research use only, and not for human or veterinary use.
Back to the topSpecifications
Product concentration: 50 mg/ml
Recommended working concentration: 100 μg/ml
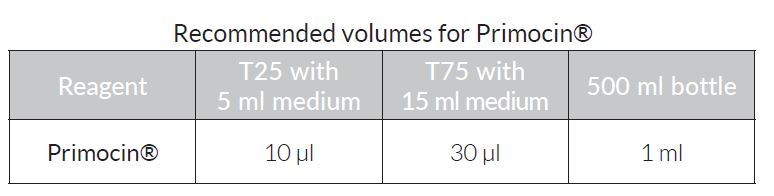
- 1 ml vial of Primocin® is sufficient for 500 ml of culture.
- 20 ml bottle of Primocin® is sufficient for 10 liters of culture.
Quality Control:
- Physicochemical characterization (pH and appearance) has been confirmed
- Endotoxin levels: < 0.5 EU/mg
- Potency has been validated on bacterial and fungal reference strains
Contents
Primocin® is provided as a cell culture tested, sterile filtered, light yellow solution at a concentration of 50 mg/ml.
This product is available in three pack sizes:
- ant-pm-05 - 5 x 1 ml vial (250 mg)
- ant-pm-1 - 10 x 1 ml vial (500 mg)
- ant-pm-2 - 1 x 20 ml bottle (1 g)
![]() Primocin® is shipped at room temperature.
Primocin® is shipped at room temperature.
![]() Upon receipt, Primocin® can be stored at 4°C for 6 months or at -20°C for long-term storage
Upon receipt, Primocin® can be stored at 4°C for 6 months or at -20°C for long-term storage
Details
Use of Primocin® in primary cell cultures
Primocin® is frequently cited in the literature for use in the protection of a number of different primary cell cultures. This includes (but is not limited to):
- Numerous human and murine primary cell cultures, including fibroblasts [1], glial cells [2], astrocytes [3], and immune cells (e.g. NK cells) [4].
- Culturing and reprogramming of human and murine embryonic cells [5] and pluripotent stem cells [6].
- 3D cell cultures including colon epithelial and carcinoma organoids [7] as well as breast, bladder, and prostate cancer organoids [8-10].
- A number of published standardized protocols such as tumor organoid-T-cell co-culture systems [11].
References:
1. Ferrer-Mayorga, G. et al., 2019. Vitamin D and Wnt3A have additive and partially overlapping modulatory effects on gene expression and phenotype in human colon fibroblasts. Sci Rep 9:8085.
2. Bussian T.J. et al., 2018. Clearance of senescent glial cells prevents tau-dependent pathology and cognitive decline. Nature. 562:578‑82.
3. Grabner, G.F. et al., 2016. Deletion of Monoglyceride Lipase in Astrocytes Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-induced Neuroinflammation. J Biol Chem 291;913‑23.
4. Garcia-Beltran, W.F. et al., 2016. Open conformers of HLA-F are high-affinity ligands of the activating NK-cell receptor KIR3DS1. Nat Immunol 17:1067-74.
5. Kogata N. et al., 2018. Sox9 regulates cell state and activity of embryonic mouse mammary progenitor cells. Commun Biol. 1:228.
6. Park S. et al., 2018. Generation of human-induced pluripotent stem cells using a defined, feeder-free reprogramming system. Curr Protoc Stem Cell Biol 45.
7. Urbischek M. et al., 2019. Organoid culture media formulated with growth factors of defined cellular activity. Sci Rep 9:6193.
8. Sachs N. et al., 2018. A living biobank of breast cancer organoids captures disease heterogeneity. Cell. 172:373-86.
9. Lee S.H. et al., 2018. Tumor evolution and drug response in patient-derived organoid models of bladder cancer. Cell 173:515-28.
10. Xu H. et al., 2018. Organoid technology and applications in cancer research. J Hematol Oncol 11:116.
11. Cattaneo, C.M. et al., 2020. Tumor organoid–T-cell coculture systems. Nat Prot 15, 15-39.